Precession driven dynamos
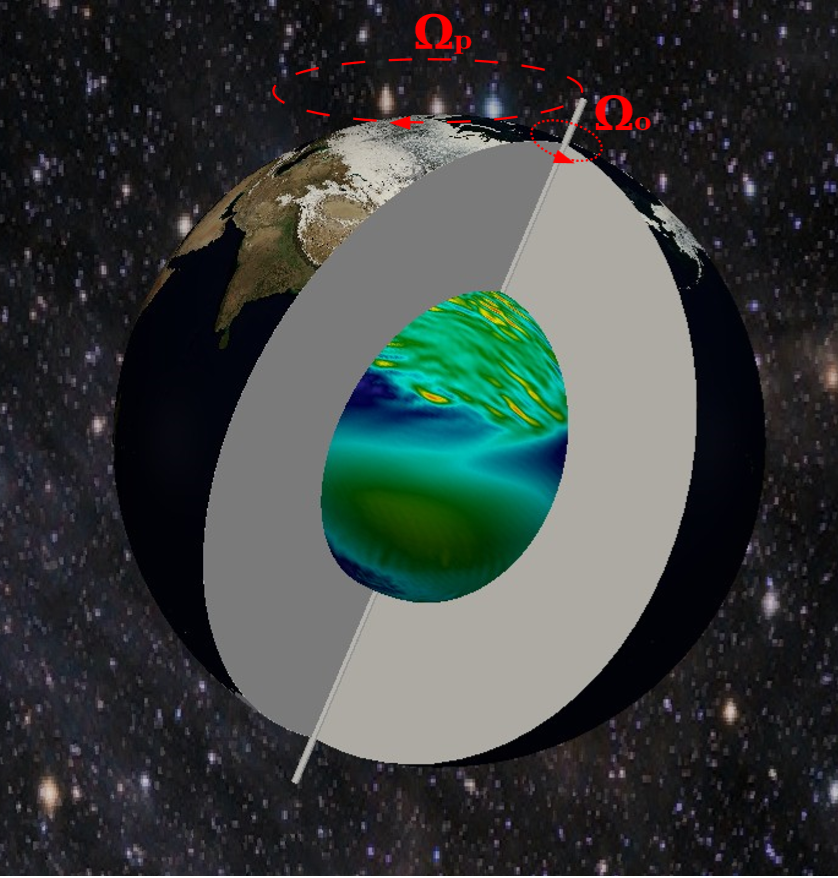
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotation axis of a rotating body. The earth goes through one full precessional period over a duration of approximately 26000 years due to the luni-solar tidal torque acting on the Earth's equatorial bulge.
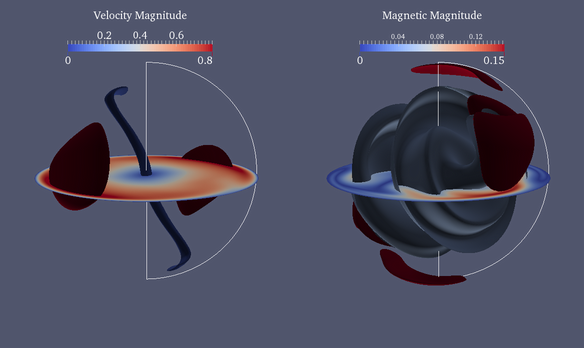
From an energetic point of view, precession is a possible driving mechanism for the generation of Earth’s magnetic field, the so-called geodynamo. We investigate precession driven dynamos in a full sphere via direct numerical simulations. A highly parallelized spectral code is used to solve the Navier-Stokes equation and magnetic field diffusion equation.
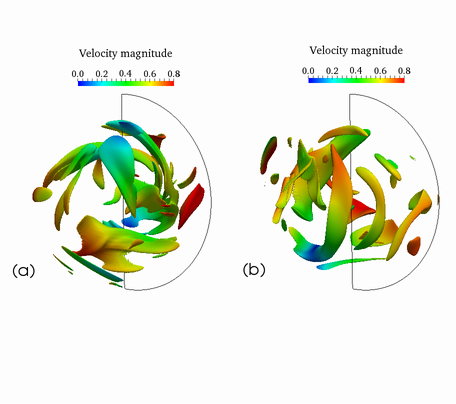
Isosurfaces of magnetic field strength rendered by the color scale of the velocity magnitude. Left: insulating boundary condition. Right: conducting boundary condition.